Pseudomeningocele after in utero repair of myelomeningocele as an early sign of hypertensive hydrocephalus – a case report and review of the literature
Pseudomeningocele after fetal surgery
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.46900/apn.v4i1(January-April).103Keywords:
Myelomeningocele, Hydrocephalus, Ventriculoperitoneal Shunt, Arnold-Chiari Malformation, Prenatal Diagnosis, Fetal SurgeryAbstract
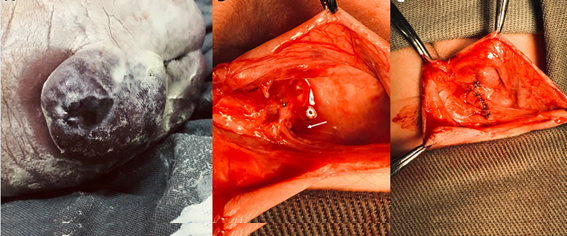
Background Myelomenigocele (MMC) is the most common congenital defect of the spine. The Management of Myelomeningocele study (MOMS trial) demonstrated that the prenatal repair decreased shunt implant, reversal of hindbrain herniation and better neurologic function compared to postnatal repair. Several ultrasound findings can predict the risk of postnatal hydrocephalus after intrauterine MMC repair. This report shows a prenatal pseudomenigocele after intrauterine correction of MMC as an early sign of hydrocephalus.
Method A 34-year-old female G2P1 with a prenatal diagnosis of MMC with anatomical level L4 and ventricular enlargement was submitted to open surgery intrauterine repair. Follow up ultrasound showed regression of the lemon sign, partial regression of hindbrain herniation and a progressive increase in the wound with local bulging characterizing a pseudomingocele. In the postnatal period, after correction of the pseudomenigocele, the neonate showed signs of hipertensive hydrocephalus. After ventriculoperitoneal shunt, the patient was discharged.
Conclusion Presence of pseudomeningocele prenatally after in utero repair of MMC may represent an early sign of hypertensive hydrocephalus.
Downloads
Additional Files
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2021 Daniel Dante Cardeal, Ingrid Schwach Werneck Britto, Sandra Rejane Silva Herbst, Milton Hikaru Toita, Gabriela Duarte Bordini, José Carlos Esteves Veiga, Rodrigo Ruano

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.

When publishing in Archives of Pediatric Neurosurgery journal, authors retain the copyright of their article and agree to license their work using a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International Public License (CC BY 4.0), thereby accepting the terms and conditions of this license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/legalcode).
The CC BY 4.0 license terms applies to both readers and the publisher and allows them to: share (copy and redistribute in any medium or format) and adapt (remix, transform, and build upon) the article for any purpose, even commercially, provided that appropriate credit is given to the authors and the journal in which the article was published.
Authors grant Archives of Pediatric Neurosurgery the right to first publish the article and identify itself as the original publisher. Under the terms of the CC BY 4.0 license, authors allow the journal to distribute the article in third party databases, as long as its original authors and citation details are identified.





























